Let’s talk about the minimum wage for a lineman. Have you ever wondered what the lowest pay is for these essential workers? Well, I’m here to shed some light on the subject. Being a lineman involves working tirelessly to install and maintain power lines, ensuring that communities have electricity. From climbing tall poles to working in extreme weather conditions, these dedicated individuals play a crucial role in keeping the lights on. But what is the minimum wage they receive for their hard work? Stick around, and we’ll uncover the answer together.
Minimum Wage for a Lineman
Definition of a Lineman
A lineman, also known as a power line worker, is a skilled professional who is responsible for installing, repairing, and maintaining electrical power systems. They work on high-voltage transmission lines, distribution lines, and substations. Linemen often face hazardous working conditions, such as working at great heights and handling live electricity. Despite these challenges, they play a crucial role in ensuring the electricity supply to homes, businesses, and industries remains uninterrupted.
Importance of Linemen
Linemen are essential to maintaining a reliable electrical infrastructure. They work tirelessly, often in adverse weather conditions, to keep power flowing to communities. Without skilled linemen, power outages would occur more frequently and last longer, leading to significant disruptions in daily life and potential safety hazards. Linemen are the unsung heroes who work behind the scenes to ensure the lights stay on and the essential machinery keeps running smoothly.
Factors Affecting Linemen Wages
Determining a lineman’s wages involves various factors that influence their earning potential. Some of the most significant factors include:
Determining Factors
Experience
Experience plays a crucial role in determining a lineman’s wages. As with most professions, linemen tend to earn higher salaries as they gain more experience in the field. Experienced linemen have acquired valuable skills and knowledge that make them more efficient and reliable in their work.
Education and Certification
Linemen are required to undergo specialized training and education to hold the necessary certifications. The more education and certifications a lineman has, the higher their earning potential. Obtaining advanced certifications and staying up-to-date with the latest industry standards and technologies can open doors to higher-paying job opportunities.
Geographical Location
The geographical location in which a lineman works significantly impacts their wages. Wages can vary greatly from state to state or even within regions of the same state. Linemen working in areas with a higher cost of living generally earn higher wages to compensate for the increased expenses associated with housing, transportation, and other necessities.
Industry and Sector
Different industries and sectors require linemen with specialized skills and expertise. Linemen working in specific sectors, such as electrical power line contracting or telecommunications, may command higher wages due to the complexity of the work involved or the demand for such specialized skills.
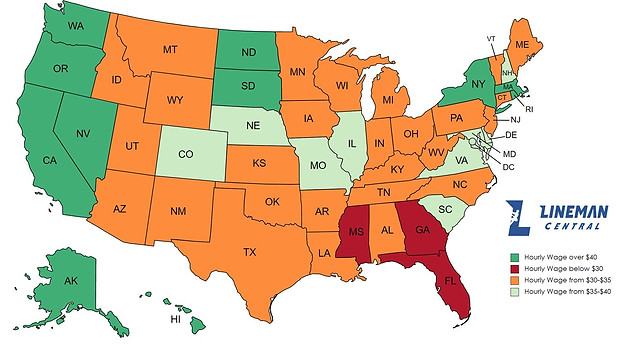
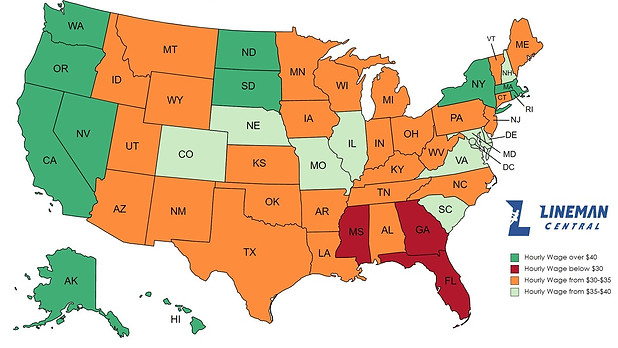
Minimum Wage Laws
To ensure workers receive fair compensation, minimum wage laws are in place at both the federal and state levels in the United States. These laws establish a baseline wage that employers must meet, ensuring that workers are paid at least a minimum amount for their services. Linemen, like any other wage-earning profession, are subject to these minimum wage laws.
Federal Minimum Wage
The federal minimum wage is the lowest hourly wage that employers must pay their employees. As of July 2021, the federal minimum wage in the United States is $7.25 per hour. However, it is important to note that some states have implemented higher minimum wage rates, which supersede the federal minimum wage if they are more favorable for the employees.
State Minimum Wage
Many states have implemented their minimum wage rates, which can differ from the federal minimum wage. These state-level minimum wage rates are typically higher to reflect the local cost of living. Linemen should refer to their specific state’s minimum wage laws to determine the minimum wage they are entitled to.
Prevailing Wage Laws
In certain circumstances, prevailing wage laws may come into play for linemen working on publicly funded projects. Prevailing wage laws require that workers on these projects are paid a wage rate that is determined by the state or federal prevailing wage survey. These rates are often higher than the minimum wage and are aimed at protecting workers and ensuring fair compensation.
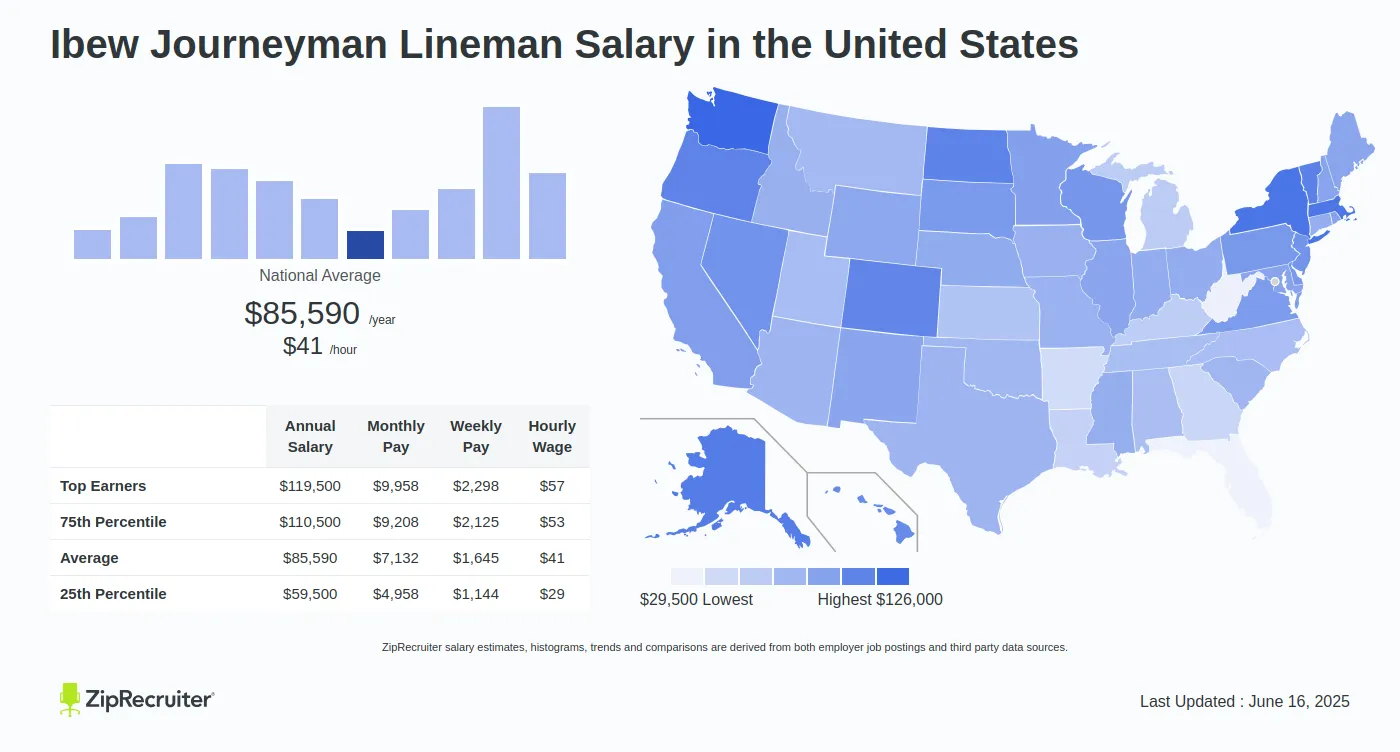
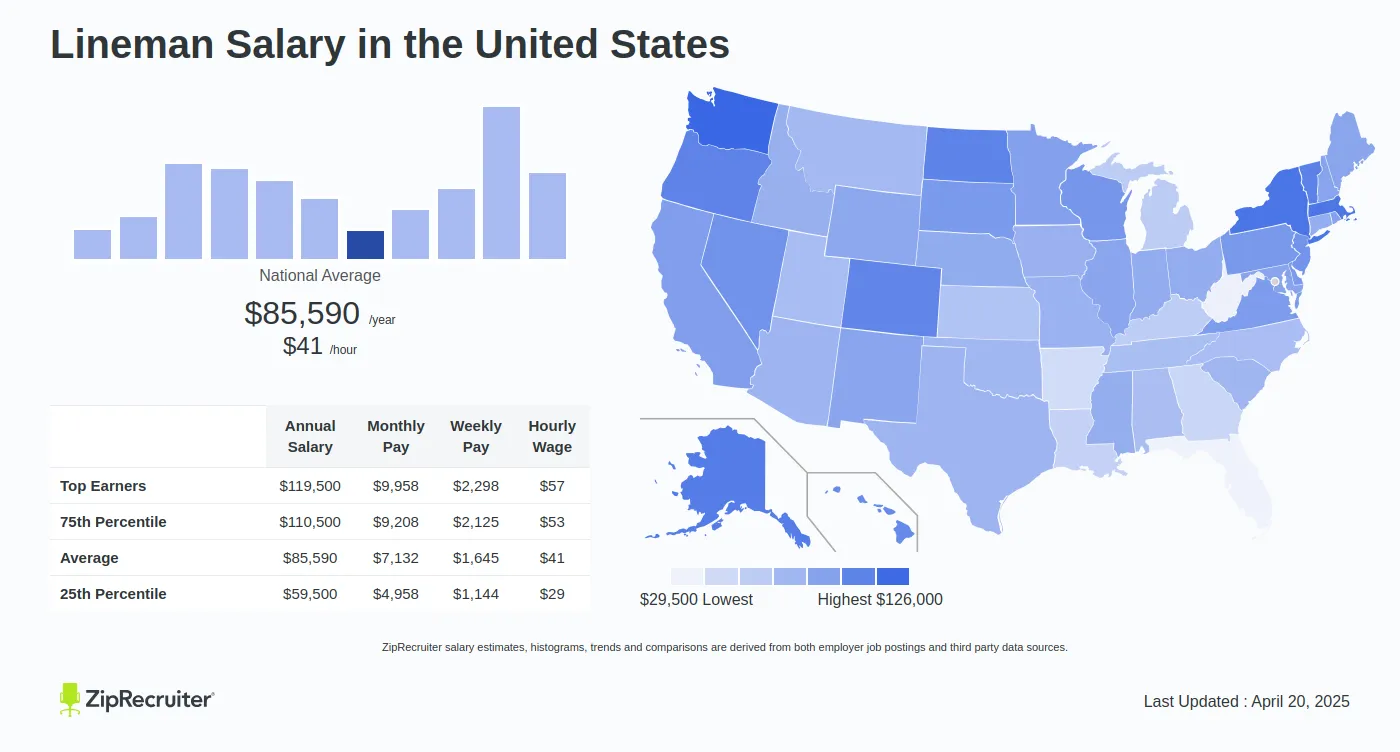
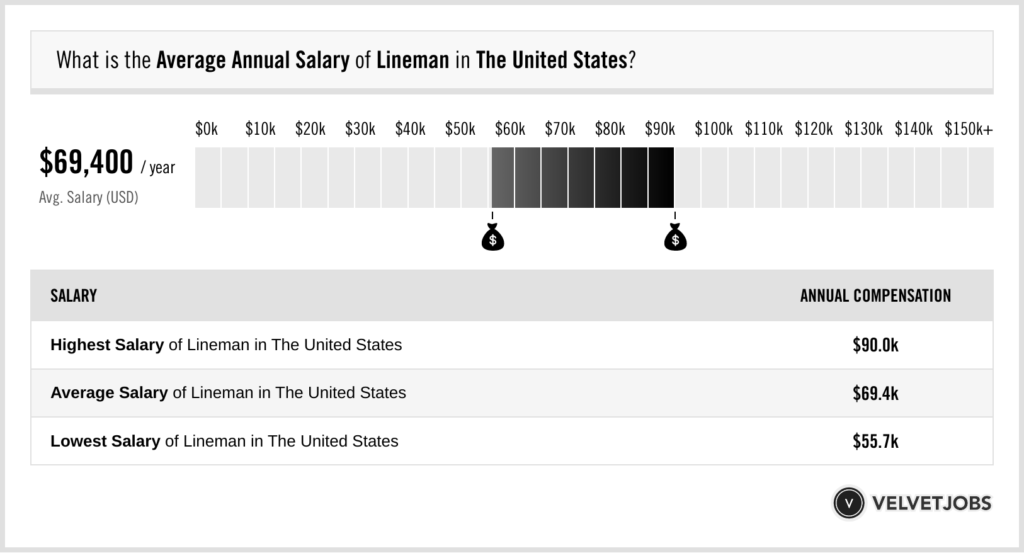
Average Lineman Salary
While minimum wage laws set a baseline for compensation, linemen, particularly those with experience and expertise, often earn salaries well above the minimum wage. The average lineman salary can vary based on several factors, including location, experience, and union affiliation.
National Average Salary
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the national average salary for electrical power-line installers and repairers (which includes linemen) was $74,500 as of May 2020. It is important to note that this figure represents the average salary across all experience levels, geographical locations, and sectors.
Unionized Linemen
Many linemen are members of labor unions, such as the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers (IBEW) or the Utility Workers Union of America (UWUA). Unionized linemen often have higher wages, as the unions negotiate collective bargaining agreements with employers to secure fair wages and benefits for their members. The collective bargaining process allows linemen to have a voice in negotiating their compensation and working conditions.
Non-Unionized Linemen
Linemen who are not part of a union may still earn competitive wages, especially if they possess extensive experience and valuable certifications. The pay scale for non-unionized linemen may vary, but they have the opportunity to negotiate wages and benefits directly with their employers.
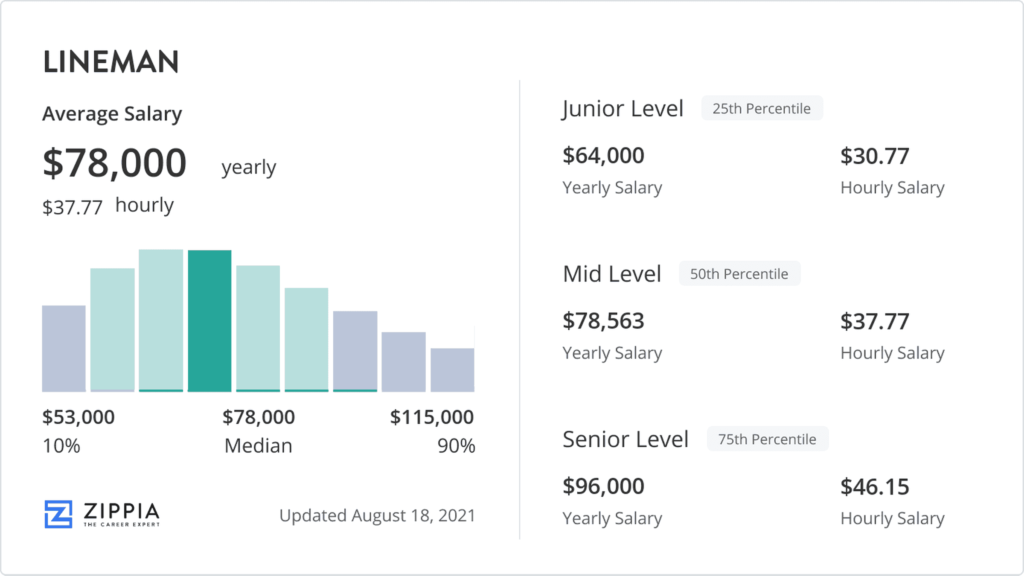
Entry-Level Lineman Wages
When starting their careers as linemen, individuals typically go through a training period or apprenticeship program to gain hands-on experience and knowledge. During this initial phase, entry-level linemen can expect to receive lower wages compared to more experienced professionals.
Training Period
During the training period, entry-level linemen often receive lower wages as they learn the ropes of the trade under the guidance of experienced linemen. This is a critical phase where apprentices gain the necessary skills to become competent linemen while earning a modest income.
Apprenticeship Programs
Apprenticeship programs are an effective way for aspiring linemen to receive on-the-job training while earning a wage. These programs typically last three to five years and involve a combination of classroom instruction and practical experience. As apprentices progress through the program, their wages gradually increase to reflect their growing expertise.
Starting Salary
The starting salary for entry-level linemen can vary depending on factors such as location, industry, and employer. On average, entry-level linemen can expect to earn around $30,000 to $40,000 per year. However, this figure can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned earlier.
Pay Scale Progression
As linemen gain experience and demonstrate their skills and reliability, they have the opportunity to progress through the pay scale and earn higher wages. Advancement within the field is often associated with increased responsibilities and supervisory roles.
Journeyman Lineman
After completing their initial training or apprenticeship program, linemen are typically classified as journeyman linemen. Journeyman linemen have successfully completed the necessary training and have attained the required certification for their specific jurisdiction. They have demonstrated their competence and are considered fully qualified to work independently. Journeyman linemen generally earn higher wages compared to entry-level linemen, often ranging from $50,000 to $80,000 per year or more, depending on various factors.
Senior Lineman
Senior linemen have gained extensive experience and expertise in their field. They are often responsible for mentoring and training apprentices and assisting with more complex projects. With their increased responsibilities, senior linemen can earn higher wages, often surpassing the six-figure mark, particularly if they have supervisory duties.
Foreman/Supervisory Positions
Some linemen progress into supervisory or foreman positions, where they oversee a team of linemen and manage projects. These positions involve additional responsibilities, such as planning and coordinating work activities, ensuring compliance with safety regulations, and overseeing the overall success of projects. Linemen in these leadership roles typically earn higher wages due to their increased responsibilities.
Additional Compensation
Beyond the base salary, linemen may receive additional compensation through various means. These additional forms of compensation contribute to the overall earning potential and attractiveness of the lineman profession.
Overtime Pay
Linemen often work long hours, including evenings, weekends, and holidays, to maintain and repair power systems. Overtime pay is typically offered for any hours worked beyond the standard 40-hour workweek. Overtime rates can vary depending on the employer and applicable labor laws, but they generally provide a higher hourly rate for the additional hours worked.
Per Diem Allowance
In some cases, linemen may be required to travel for work or take on assignments away from their home base. Employers may offer a per diem allowance to cover expenses such as lodging, meals, and transportation while on these assignments. This additional allowance helps offset the costs associated with living away from home and can significantly boost a lineman’s overall compensation.
Benefits and Perks
Employers often provide additional benefits and perks to attract and retain linemen. These benefits can include comprehensive healthcare coverage, retirement plans, paid time off, and various forms of insurance coverage. The value of these benefits and perks adds to a lineman’s overall compensation package and can enhance their quality of life.
Industry and Sector Variations
Linemen work in various industries and sectors, and the nature of their work can influence their wages. The following are a few examples of industry and sector variations that can impact lineman wages:
Electrical Power Line Contractors
Linemen working for electrical power line contractors may have the opportunity to work on different types of projects, including new installations, maintenance and repair work, or upgrading existing infrastructure. The complexity and scale of these projects can impact wages, with larger and more intricate projects often commanding higher wages due to the specialized skills and expertise required.
Telecommunications
With the growing demand for reliable and efficient communication networks, linemen working in the telecommunications sector play a vital role in installing and maintaining telecommunication lines and equipment. The unique skill set required for this sector can result in higher wages compared to other industries.
Utility Companies
Linemen employed by utility companies, such as electric utility providers, have the responsibility of ensuring uninterrupted power supply to homes and businesses. The essential nature of their work often translates into competitive wages to attract and retain skilled linemen who can handle the unique demands and challenges of the utility industry.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Linemen who strive for career growth and increased earning potential can explore various avenues for advancement within the field. These opportunities allow linemen to expand their knowledge and skills and take on roles with higher levels of responsibility.
Further Education and Certifications
Continuing education and pursuing additional certifications can open doors to higher-paying positions and specialized roles within the industry. Linemen may choose to pursue advanced certifications in areas such as electrical systems design, power quality analysis, or specialized equipment operation. These certifications showcase expertise and dedication, making linemen more valuable to employers and increasing their earning potential.
Specialized Skills
Becoming proficient in specialized skills, such as working with live wires, performing high-voltage splicing, or dealing with sophisticated metering equipment, can lead to higher wages. Linemen who possess these specialized skills are often in high demand and may have opportunities for higher-paying positions or contract work.
Management Positions
Some linemen who aspire to move away from the hands-on aspect of the job can pursue management positions within the industry. These roles involve overseeing teams of linemen, coordinating projects, and managing budgets. Management positions can come with higher salaries and increased benefits due to the level of responsibility and leadership required.
Future Outlook for Linemen Wages
Several factors indicate positive prospects for linemen wages in the future. These factors include industry growth and demand, technological advancements, and union negotiations.
Industry Growth and Demand
The increasing global demand for electricity and the expansion of infrastructure projects contribute to the growth of the lineman profession. As new power generation facilities, transmission lines, and distribution networks are built, linemen will continue to play a crucial role. This growth in demand is likely to lead to increased wages as companies compete for skilled linemen.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in the energy sector, such as the integration of renewable energy sources and the development of smart grids, require linemen to adapt and learn new skills. Linemen who keep up with technological advancements through additional training and education are likely to command higher wages due to their ability to meet the demands of this evolving industry.
Union Negotiations
Union negotiations play a significant role in determining wages and benefits for linemen. As unions advocate for fair compensation and improved working conditions, the bargaining power of linemen increases. Collective bargaining agreements often result in higher wages, improved benefits, and greater job security for unionized linemen.
In conclusion, while the minimum wage for a lineman is subject to federal and state laws, a lineman’s earning potential is influenced by several factors. Factors such as experience, education, geographical location, and industry can impact wages significantly. Additionally, entry-level wages are typically lower during the training period, but wages increase as linemen gain experience and progress through the profession. Various forms of additional compensation, including overtime pay, per diem allowances, and benefits, contribute to a lineman’s overall earning potential. With the projected growth in the industry, advancements in technology, and ongoing union negotiations, the future looks promising for linemen wages. Linemen contribute greatly to society by ensuring a reliable power supply, and their wages should reflect the importance and demands of their profession.